1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
| import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
import torch, yaml, cv2, os, shutil
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm import trange
from PIL import Image
from ultralytics.nn.tasks import DetectionModel as Model
from ultralytics.utils.torch_utils import intersect_dicts
from ultralytics.utils.ops import xywh2xyxy
from pytorch_grad_cam import GradCAMPlusPlus, GradCAM, XGradCAM
from pytorch_grad_cam.utils.image import show_cam_on_image
from pytorch_grad_cam.activations_and_gradients import ActivationsAndGradients
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(114, 114, 114), auto=True, scaleFill=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):
shape = im.shape[:2]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup:
r = min(r, 1.0)
ratio = r, r
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1]
if auto:
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, stride), np.mod(dh, stride)
elif scaleFill:
dw, dh = 0.0, 0.0
new_unpad = (new_shape[1], new_shape[0])
ratio = new_shape[1] / shape[1], new_shape[0] / shape[0]
dw /= 2
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad:
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color)
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
class yolov8_heatmap:
def __init__(self, weight, cfg, device, method, layer, backward_type, conf_threshold, ratio):
device = torch.device(device)
ckpt = torch.load(weight)
model_names = ckpt['model'].names
csd = ckpt['model'].float().state_dict()
model = Model(cfg, ch=3, nc=len(model_names)).to(device)
csd = intersect_dicts(csd, model.state_dict(), exclude=['anchor'])
model.load_state_dict(csd, strict=False)
model.eval()
print(f'Transferred {len(csd)}/{len(model.state_dict())} items')
target_layers = [eval(layer)]
method = eval(method)
colors = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(model_names), 3)).astype(np.int32)
self.__dict__.update(locals())
def post_process(self, result):
logits_ = result[:, 4:]
boxes_ = result[:, :4]
sorted, indices = torch.sort(logits_.max(1)[0], descending=True)
return torch.transpose(logits_[0], dim0=0, dim1=1)[indices[0]], torch.transpose(boxes_[0], dim0=0, dim1=1)[indices[0]], xywh2xyxy(torch.transpose(boxes_[0], dim0=0, dim1=1)[indices[0]]).cpu().detach().numpy()
def draw_detections(self, box, color, name, img):
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = list(map(int, list(box)))
cv2.rectangle(img, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), tuple(int(x) for x in color), 2)
cv2.putText(img, str(name), (xmin, ymin - 5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.8, tuple(int(x) for x in color), 2, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
return img
def __call__(self, img_path, save_path):
if os.path.exists(save_path):
shutil.rmtree(save_path)
os.makedirs(save_path, exist_ok=True)
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = letterbox(img)[0]
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = np.float32(img) / 255.0
tensor = torch.from_numpy(np.transpose(img, axes=[2, 0, 1])).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device)
grads = ActivationsAndGradients(self.model, self.target_layers, reshape_transform=None)
result = grads(tensor)
activations = grads.activations[0].cpu().detach().numpy()
post_result, pre_post_boxes, post_boxes = self.post_process(result[0])
for i in trange(int(post_result.size(0) * self.ratio)):
if float(post_result[i].max()) < self.conf_threshold:
break
self.model.zero_grad()
if self.backward_type == 'class' or self.backward_type == 'all':
score = post_result[i].max()
score.backward(retain_graph=True)
if self.backward_type == 'box' or self.backward_type == 'all':
for j in range(4):
score = pre_post_boxes[i, j]
score.backward(retain_graph=True)
if self.backward_type == 'class':
gradients = grads.gradients[0]
elif self.backward_type == 'box':
gradients = grads.gradients[0] + grads.gradients[1] + grads.gradients[2] + grads.gradients[3]
else:
gradients = grads.gradients[0] + grads.gradients[1] + grads.gradients[2] + grads.gradients[3] + grads.gradients[4]
b, k, u, v = gradients.size()
weights = self.method.get_cam_weights(self.method, None, None, None, activations, gradients.detach().numpy())
weights = weights.reshape((b, k, 1, 1))
saliency_map = np.sum(weights * activations, axis=1)
saliency_map = np.squeeze(np.maximum(saliency_map, 0))
saliency_map = cv2.resize(saliency_map, (tensor.size(3), tensor.size(2)))
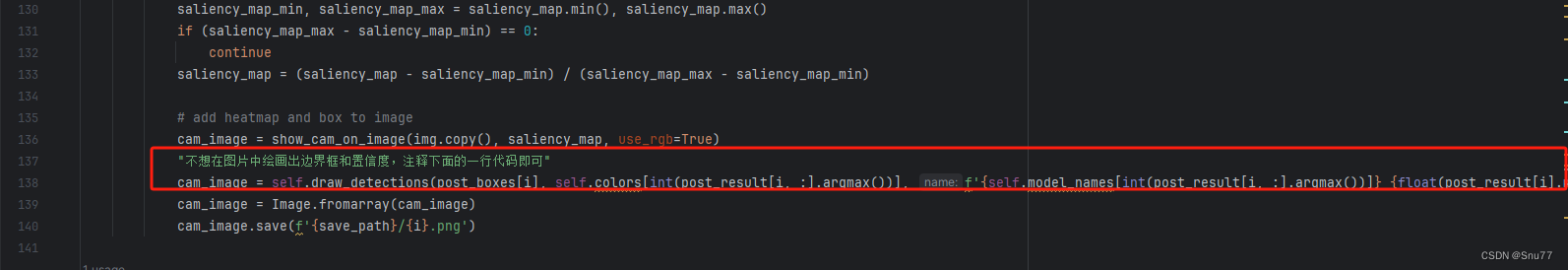
saliency_map_min, saliency_map_max = saliency_map.min(), saliency_map.max()
if (saliency_map_max - saliency_map_min) == 0:
continue
saliency_map = (saliency_map - saliency_map_min) / (saliency_map_max - saliency_map_min)
cam_image = show_cam_on_image(img.copy(), saliency_map, use_rgb=True)
"不想在图片中绘画出边界框和置信度,注释下面的一行代码即可"
cam_image = self.draw_detections(post_boxes[i], self.colors[int(post_result[i, :].argmax())], f'{self.model_names[int(post_result[i, :].argmax())]} {float(post_result[i].max()):.2f}', cam_image)
cam_image = Image.fromarray(cam_image)
cam_image.save(f'{save_path}/{i}.png')
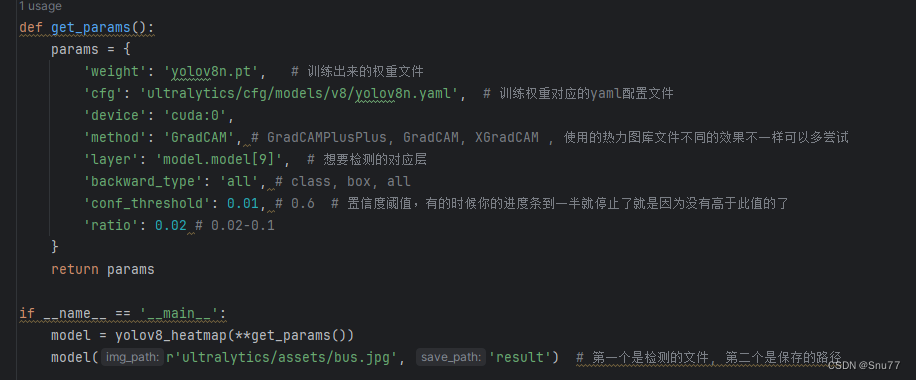
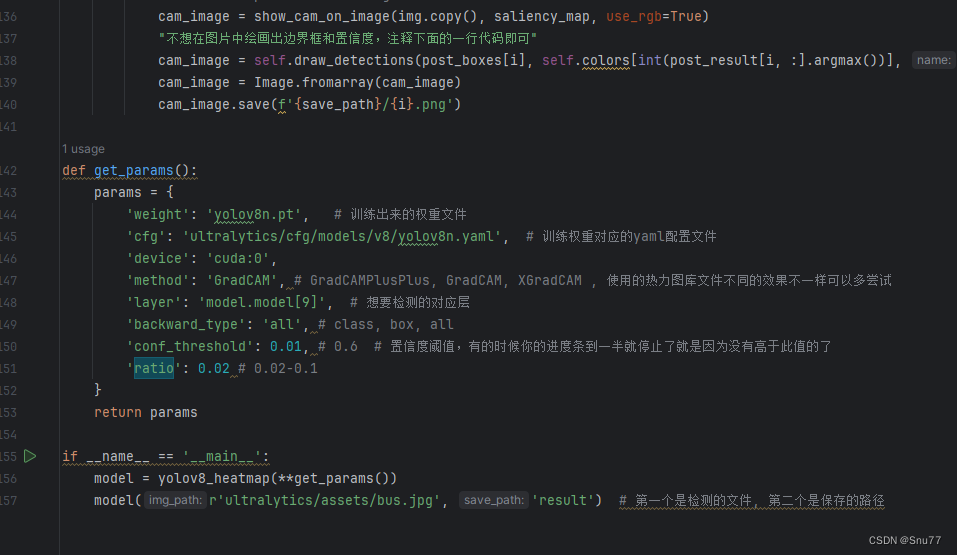
def get_params():
params = {
'weight': 'yolov8n.pt',
'cfg': 'ultralytics/cfg/models/v8/yolov8n.yaml',
'device': 'cuda:0',
'method': 'GradCAM',
'layer': 'model.model[9]',
'backward_type': 'all',
'conf_threshold': 0.01,
'ratio': 0.02
}
return params
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = yolov8_heatmap(**get_params())
model(r'ultralytics/assets/bus.jpg', 'result')
|